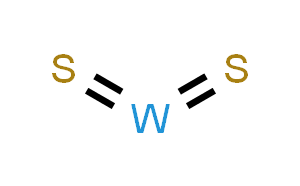Novel effects can occur in materials when structures are formed with sizes comparable to any one of many possible length scales, such as the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, or the optical wavelengths of high energy photons. In these cases quantum mechanical effects can dominate material properties. One example is quantum confinement where the electronic properties of solids are altered with great reductions in particle size. The optical properties of nanoparticles, e.g. fluorescence, also become a function of the particle diameter. This effect does not come into play by going from macrosocopic to micrometer dimensions, but becomes pronounced when the nanometer scale is reached.
In addition to optical and electronic properties, the novel mechanical properties of many nanomaterials is the subject of nanomechanics research. When added to a bulk material, nanoparticles can strongly influence the mechanical properties of the material, such as the stiffness or elasticity. For example, traditional polymers can be reinforced by nanoparticles (such as carbon nanotubes) resulting in novel materials which can be used as lightweight replacements for metals. Such composite materials may enable a weight reduction accompanied by an increase in stability and improved functionality.
Finally, nanostructured materials with small particle size such as zeolites, and asbestos, are used as catalysts in a wide range of critical industrial chemical reactions. The further development of such catalysts can form the basis of more efficient, environmentally friendly chemical processes.